A Survey of the Prophets - Hosea
|
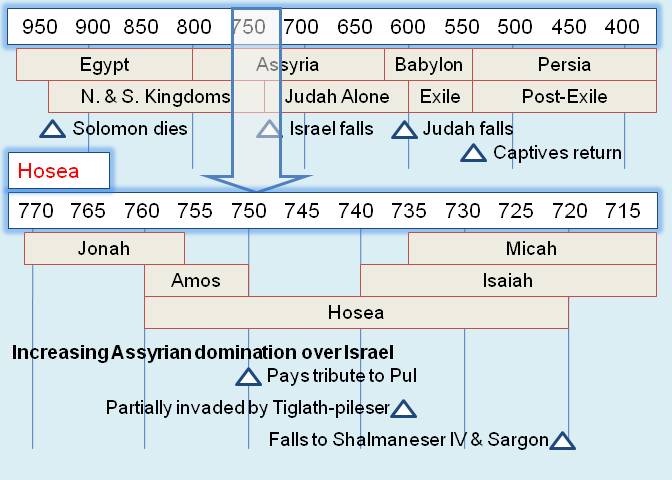
Historical Background of the Book. Despite warnings from the prophet Amos around 760 B.C., the Northern Kingdom of Israel continued in their idolatry and immorality. To the east, the Assyrians were rising in power and expanding westward after Jonah's visit around 770 B.C.. In 750 B.C. they would begin extracting tribute from Israel (2 Kings 15:19). 15 years later around 735 B.C., the Assyrians would partially invade the land under Tiglath-pileser (2 Kings 15:29). Finally, around 720 B.C. the Northern Kingdom would fall to the Assyrians under Shalmaneser IV and Sargon. The Israelites would be scattered throughout the Assyrian Empire and their land inhabited by others from the Empire. These foreigners would eventually become the Samaritans who hindered the rebuilding of the temple by Zerubabbel around 535 B.C. (Ezra 4:1-2), hindered the rebuilding of Jerusalem's walls by Nehemiah around 445 B.C. (Neh. 4:1-2), were the object of racism in Jesus' day around 30 A.D. (John 4:9; 8:48).
|
The Author and the Audience. Hosea was from the Northern Kingdom. Some scholars believe he was from the tribe of Isaachar. As a contemporary of Jonah, Amos, Isaiah, and Micah, Hosea tried to deliver God's message over about a 40 year span from roughly 760 B.C. to 720 B.C. His primary audience was Ephraim, the largest northern tribe and likely representative of the whole Northern Kingdom. However, Judah is also frequently mentioned.
Outline/Major Themes. Hosea delivered much of God's message as a "living parable".:
Outline/Major Themes. Hosea delivered much of God's message as a "living parable".:
- Ch. 1-3 Hosea was commanded by God to marry Gomer, a prostitute. Together they had three children whose names were significant of God's relationship with Israel: Jezreel ("scattered by God"), Lo-ruhamah ("not pitied"), and Lo-ammi ("not my people"). Gomer returned to a life of prostitution and slavery. Hosea was commanded to buy her back.
- Ch. 4-7 Israel's unfaithfulness is described in terms of physical and spiritual adultery. Instead of relying on God for protection from the growing Assyrian empire, they used bribery (2 Kings 15:19-20).
- Ch. 8-10 Prophecies of Israel's pending punishment.
- Ch. 11-14 The Lord is still faithful and willing to forgive.
- Spiritual adultery includes friendship with the world (James 4:4) as well as mixing true and false worship (Matt. 15:1-9).
- Love for God's word is needed as a foundational attitude (Ch. 4:6; 2 Thes. 2:10-12).
- God still loves us, even when we are sinful (John 3:16).
- We need persistence in the face of evil (Gal. 6:9).